Initial LSTM Java Testing
Testing the training of the AI model with example code
This is our initial test with LSTM. Here we do our initial data collection from Yahoo finance and use it to attempt to train and test our model and it’s accuracy.
Data Collection
Collecting data with Python.
We use a Yahoo Finance library to collect the data for the stocks from the previous 20 years. We store the data in a CSV file.
import yfinance as yf # library for data
import pandas as pd
tickers = ["GOOGL", "AMZN", "AAPL", "TSLA", "WMT", "MSFT", "META", "COST", "LMT", "NOC", "UNH"] # tickers for data collecting
for ticker in tickers: # iterating through each stock
print("Processing ticker: ", ticker)
data = yf.download(ticker, start="2004-01-01", end="2024-01-22") # gathering data
csv_data = data.to_csv(path_or_buf=f"./stock_data/{ticker}.csv") # data files
Viewing Data
This is how we view the data that we have gathered, in a more pleasant format.
We use a java charting tool to chart the data and display it for future use when comparing our predicted data to our real data.
// libraries and imports needed to create the graphs as images
%maven org.jfree:jfreechart:1.5.3
%maven com.opencsv:opencsv:5.5
import org.jfree.chart.ChartFactory;
import org.jfree.chart.ChartUtils;
import org.jfree.chart.JFreeChart;
import org.jfree.data.category.CategoryDataset;
import org.jfree.data.category.DefaultCategoryDataset;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.FileReader;
public class JFreeChartExample {
// gathering data from the CSV files
public static CategoryDataset createDataset(String ticker){
DefaultCategoryDataset dataset = new DefaultCategoryDataset();
// csv data for stocks
String csvFilePath = "./stock_data/" + ticker + ".csv";
try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(csvFilePath))) {
int dateColumnIndex = 0;
int closeColumnIndex = 6;
String line = br.readLine();
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
String[] data = line.split(",");
String date = data[dateColumnIndex];
Double close = Double.parseDouble(data[closeColumnIndex]);
// iterating through the necessary data in the CSV
dataset.addValue(close, ticker, date);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return dataset;
}
// charting the data
public static JFreeChart createChart(CategoryDataset dataset, String ticker, String val1, String val2) {
String title = val1 + " vs. " + val2 + " for " + ticker;
// creating a visual graph of the data using a charting library
return ChartFactory.createLineChart(
title,
val1,
val2,
dataset
);
}
// saving the chart as an image
public static void saveChartAsImage(JFreeChart chart, String filePath, int width, int height) throws IOException {
ChartUtils.saveChartAsPNG(new File(filePath), chart, width, height);
}
// running classes to graph data
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
String[] tickers = {"AAPL", "AMZN", "COST", "GOOGL", "LMT", "META", "MSFT", "NOC", "TSLA", "UNH", "WMT"};
for (String ticker : tickers) {
// running through charting methosd to create images of data
CategoryDataset dataset = createDataset(ticker);
JFreeChart chart = createChart(dataset, ticker, "Date", "Volume");
String chartname = "./stock_charts/date_vs_volume/" + ticker + "_chart.png";
// Save chart as image
saveChartAsImage(chart, chartname, 800, 600);
System.out.println("Chart saved as image: " + chartname);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
JFreeChartExample.main(null);
Chart saved as image: ./stock_charts/date_vs_volume/AAPL_chart.png
Chart saved as image: ./stock_charts/date_vs_volume/AMZN_chart.png
Chart saved as image: ./stock_charts/date_vs_volume/COST_chart.png
Chart saved as image: ./stock_charts/date_vs_volume/GOOGL_chart.png
Chart saved as image: ./stock_charts/date_vs_volume/LMT_chart.png
Chart saved as image: ./stock_charts/date_vs_volume/META_chart.png
Chart saved as image: ./stock_charts/date_vs_volume/MSFT_chart.png
Chart saved as image: ./stock_charts/date_vs_volume/NOC_chart.png
Chart saved as image: ./stock_charts/date_vs_volume/TSLA_chart.png
Chart saved as image: ./stock_charts/date_vs_volume/UNH_chart.png
Chart saved as image: ./stock_charts/date_vs_volume/WMT_chart.png
Create testing and training datasets
This is where we begin implementing LSTM
First we need to train the LSTM model in order to be able to predict future results. After training the model, we need to test whether our predicted values line up with the actual values of the stock data, allowing us to verify that our data is accurate.
You may be wondering: What is LSTM? Here’s a brief explanation:
What is LSTM?
LSTM stands for Long Short-Term Memory, which is based off a RNN (Recurrent Neural Network). A recurring neural network works very similarly to how our brains work, looking back on previous data from a short time period and predicting what will happen in the future based on that data.
The Problem: RNN
An RNN is a Recurrent Neural Network, which is able to look through a short amount of information and make inferences based on this information. Keywords: short-term memory. An RNN is simply unable to handle the amount of information required for stock prediction because it only works on a short term basis. Because of this, very important information from the beginning is left out, which is essential to successfully predicting stock data.
This is largely due to back propagation, which in short is the gradient value (the values used to update the neural networks weights) disappearing as time goes on. When the gradient value becomes smaller and smaller, this results in not much learning happening based on the data to which the weight is assigned to. This leads to that data being ignored and therefore not being used later on to accurately predict the future data.
The Solution: LSTMs and GRUs

In the image above, you can see how an LSTM and GRU functions. Ignore the GRU portion, as it is not used in our model.
Going back to how an RNN functions, it takes in previous data, in the form of vectors, which are passed through the RNN processes.
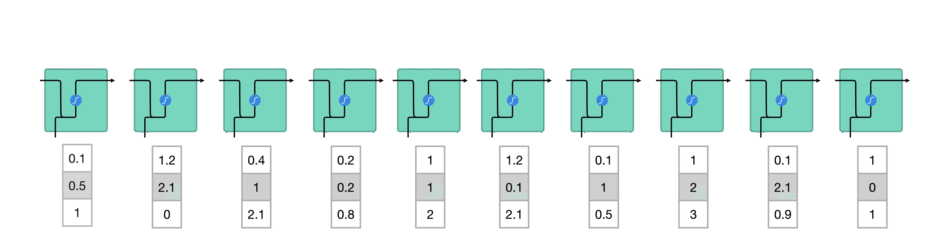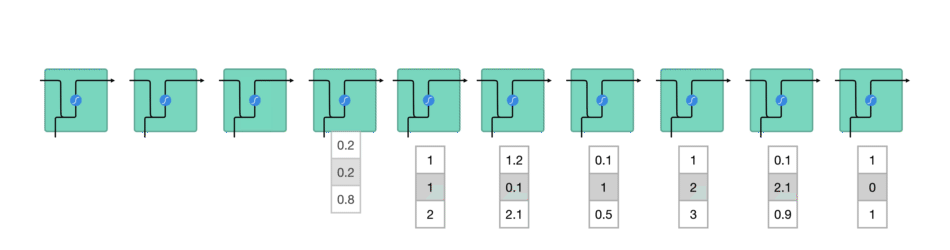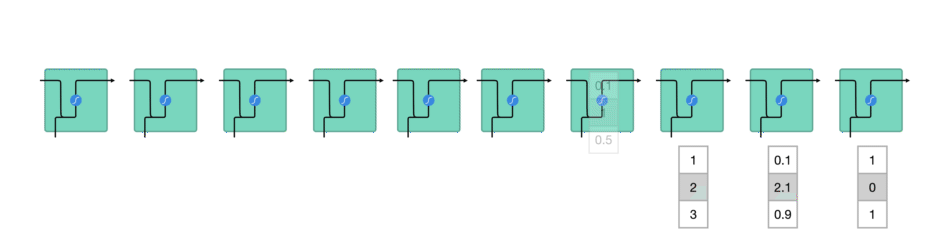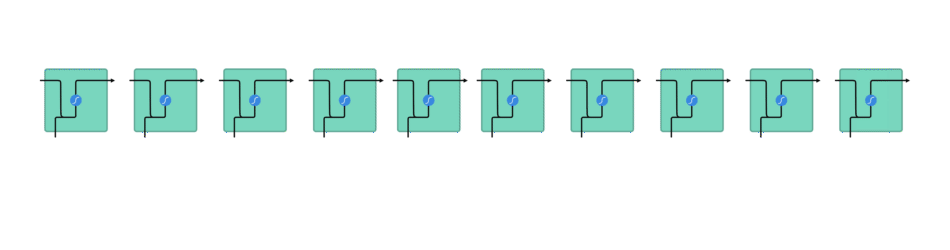
%maven org.nd4j:nd4j-native-platform:1.0.0-beta2
%maven org.deeplearning4j:deeplearning4j-core:1.0.0-beta2
%maven org.deeplearning4j:deeplearning4j-ui_2.11:1.0.0-beta2
%maven ch.qos.logback:logback-classic:1.2.3
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import org.deeplearning4j.eval.ROC;
import org.deeplearning4j.nn.multilayer.MultiLayerNetwork;
import org.deeplearning4j.util.ModelSerializer;
import org.nd4j.linalg.api.ndarray.INDArray;
import org.nd4j.linalg.dataset.DataSet;
import org.nd4j.linalg.dataset.api.iterator.DataSetIterator;
import org.nd4j.linalg.dataset.api.preprocessor.NormalizerMinMaxScaler;
import org.nd4j.linalg.factory.Nd4j;
import org.jfree.data.category.CategoryDataset;
import org.jfree.data.category.DefaultCategoryDataset;
import com.nighthawk.spring_portfolio.mvc.lstm.LSTMGraph;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.ToString;
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@ToString
@Data
public class LSTMTrainerTester {
private String file;
private double splitRatio;
private int labelIndex;
private int features; //5
private int labels; // 1
private int batchSize; //32
private int stepCount; //1
private ROC roc;
private DataSetIterator iterator;
public LSTMTrainerTester(String directory, String ticker, int features, int labels, int batchSize, int stepCount) {
this.file = directory + "/" + ticker + "_test.csv";
this.features = features;
this.labels = labels;
this.batchSize = batchSize;
this.stepCount = stepCount;
this.roc = new ROC(100);
}
public void TrainAndTestModel(MultiLayerNetwork net) {
ArrayList<Double> actual = new ArrayList<Double>();
ArrayList<Double> predicted = new ArrayList<Double>();
NormalizerMinMaxScaler minMaxScaler = new NormalizerMinMaxScaler(0,1);
try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file))) {
String line = br.readLine();
System.out.println(line);
for (int i = 0; i < 32*100; i++) {
line = br.readLine();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i ++) {
double[][][] featureMatrix = new double[batchSize][this.features][this.stepCount];
double[][][] labelsMatrix = new double[batchSize][this.labels][this.stepCount];
for (int batch = 0; batch < this.batchSize; batch++) {
line = br.readLine();
String[] values = line.split(",");
featureMatrix[batch][0][0] = Double.parseDouble(values[1]); // OPEN
featureMatrix[batch][1][0] = Double.parseDouble(values[2]); // HIGH
featureMatrix[batch][2][0] = Double.parseDouble(values[3]); // LOW
labelsMatrix[batch][0][0] = Double.parseDouble(values[4]); // CLOSE
}
INDArray featuresArray = Nd4j.create(featureMatrix);
INDArray labelsArray = Nd4j.create(labelsMatrix);
DataSet train = new DataSet(featuresArray, labelsArray);
minMaxScaler.fit(train);
// System.out.println(train);
net.fit(train);
net.rnnClearPreviousState();
}
for (int i = 0; i<1; i++) {
double[][][] featureMatrix = new double[batchSize][this.features][this.stepCount];
double[][][] labelsMatrix = new double[batchSize][this.labels][this.stepCount];
for (int batch = 0; batch < this.batchSize; batch++) {
line = br.readLine();
String[] values = line.split(",");
featureMatrix[batch][0][0] = Double.parseDouble(values[1]); // OPEN
featureMatrix[batch][1][0] = Double.parseDouble(values[2]); // HIGH
featureMatrix[batch][2][0] = Double.parseDouble(values[3]); // LOW
labelsMatrix[batch][0][0] = Double.parseDouble(values[4]); // CLOSE
}
INDArray featuresArray = Nd4j.create(featureMatrix);
INDArray labelsArray = Nd4j.create(labelsMatrix);
DataSet test = new DataSet(featuresArray, labelsArray);
minMaxScaler.fit(test);
INDArray output = net.output(test.getFeatures());
for (int j = 0; j < this.batchSize; j++) {
actual.add(test.getLabels().getDouble(j,0,0));
predicted.add(output.getDouble(j,0,0));
}
roc.evalTimeSeries(test.getLabels(), output);
}
System.out.println("Output: ");
System.out.println(predicted);
System.out.println("Actual: ");
System.out.println(actual);
System.out.println("FINAL TEST AUC: " + roc.calculateAUC());
File locationToSave = new File("src/main/java/com/nighthawk/spring_portfolio/mvc/lstm/resources/StockPriceLSTM_".concat("CLOSE").concat(".zip"));
ModelSerializer.writeModel(net, locationToSave, true);
LSTMGraph plotter = new LSTMGraph(actual, predicted);
System.out.println("Image created");
net = ModelSerializer.restoreMultiLayerNetwork(locationToSave);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Testing code for LSTM
import org.deeplearning4j.datasets.iterator.impl.*;
import org.deeplearning4j.nn.api.OptimizationAlgorithm;
import org.deeplearning4j.nn.conf.GradientNormalization;
import org.deeplearning4j.nn.conf.NeuralNetConfiguration;
import org.deeplearning4j.nn.conf.layers.LSTM;
import org.deeplearning4j.nn.conf.layers.RnnOutputLayer;
import org.deeplearning4j.nn.multilayer.MultiLayerNetwork;
import org.deeplearning4j.nn.weights.WeightInit;
import org.deeplearning4j.optimize.listeners.ScoreIterationListener;
import org.nd4j.linalg.activations.Activation;
import org.nd4j.linalg.dataset.api.iterator.DataSetIterator;
import org.nd4j.linalg.learning.config.Adam;
import org.nd4j.linalg.lossfunctions.LossFunctions;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class LstmExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Define your dataset and load it
// Example: List<double[]> features = loadFeatures();
// List<double[]> labels = loadLabels();
// Create DataSetIterator
DataSetIterator iterator = new ListDataSetIterator<>(createData(features, labels));
// Neural network configuration
MultiLayerNetwork model = new MultiLayerNetwork(new NeuralNetConfiguration.Builder()
.seed(123)
.optimizationAlgo(OptimizationAlgorithm.STOCHASTIC_GRADIENT_DESCENT)
.updater(new Adam(0.01))
.l2(1e-4)
.weightInit(WeightInit.XAVIER)
.gradientNormalization(GradientNormalization.ClipElementWiseAbsoluteValue)
.gradientNormalizationThreshold(0.5)
.list()
.layer(new LSTM.Builder()
.nIn(numInputs)
.nOut(numHiddenUnits)
.activation(Activation.TANH)
.build())
.layer(new RnnOutputLayer.Builder(LossFunctions.LossFunction.MSE)
.activation(Activation.IDENTITY)
.nIn(numHiddenUnits)
.nOut(numOutputs)
.build())
.pretrain(false)
.backprop(true)
.build()
);
model.init();
model.setListeners(new ScoreIterationListener(20)); // Print the score with every 20 iterations
// Train the model
int numEpochs = 50;
for (int i = 0; i < numEpochs; i++) {
model.fit(iterator);
}
// Your model is now trained and ready for prediction
}
private static List<DataSet> createData(List<double[]> features, List<double[]> labels) {
List<DataSet> dataSets = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < features.size(); i++) {
dataSets.add(new DataSet(Nd4j.create(features.get(i)), Nd4j.create(labels.get(i))));
}
return dataSets;
}
// Implement methods to load your features and labels from your dataset
// private static List<double[]> loadFeatures() { ... }
// private static List<double[]> loadLabels() { ... }
}
| public class LstmExample {
|
| public static void main(String[] args) {
| // Define your dataset and load it
| // Example: List<double[]> features = loadFeatures();
| // List<double[]> labels = loadLabels();
|
| // Create DataSetIterator
| DataSetIterator iterator = new ListDataSetIterator<>(createData(features, labels));
|
| // Neural network configuration
| MultiLayerNetwork model = new MultiLayerNetwork(new NeuralNetConfiguration.Builder()
| .seed(123)
| .optimizationAlgo(OptimizationAlgorithm.STOCHASTIC_GRADIENT_DESCENT)
| .updater(new Adam(0.01))
| .l2(1e-4)
| .weightInit(WeightInit.XAVIER)
| .gradientNormalization(GradientNormalization.ClipElementWiseAbsoluteValue)
| .gradientNormalizationThreshold(0.5)
| .list()
| .layer(new LSTM.Builder()
| .nIn(numInputs)
| .nOut(numHiddenUnits)
| .activation(Activation.TANH)
| .build())
| .layer(new RnnOutputLayer.Builder(LossFunctions.LossFunction.MSE)
| .activation(Activation.IDENTITY)
| .nIn(numHiddenUnits)
| .nOut(numOutputs)
| .build())
| .pretrain(false)
| .backprop(true)
| .build()
| );
|
| model.init();
| model.setListeners(new ScoreIterationListener(20)); // Print the score with every 20 iterations
|
| // Train the model
| int numEpochs = 50;
| for (int i = 0; i < numEpochs; i++) {
| model.fit(iterator);
| }
|
| // Your model is now trained and ready for prediction
| }
|
| private static List<DataSet> createData(List<double[]> features, List<double[]> labels) {
| List<DataSet> dataSets = new ArrayList<>();
| for (int i = 0; i < features.size(); i++) {
| dataSets.add(new DataSet(Nd4j.create(features.get(i)), Nd4j.create(labels.get(i))));
| }
| return dataSets;
| }
|
| // Implement methods to load your features and labels from your dataset
| // private static List<double[]> loadFeatures() { ... }
| // private static List<double[]> loadLabels() { ... }
| }
Unresolved dependencies:
- class DataSet
- class ListDataSetIterator
- variable features
- variable labels
- variable numHiddenUnits
- variable numInputs
- variable numOutputs
- variable Nd4j